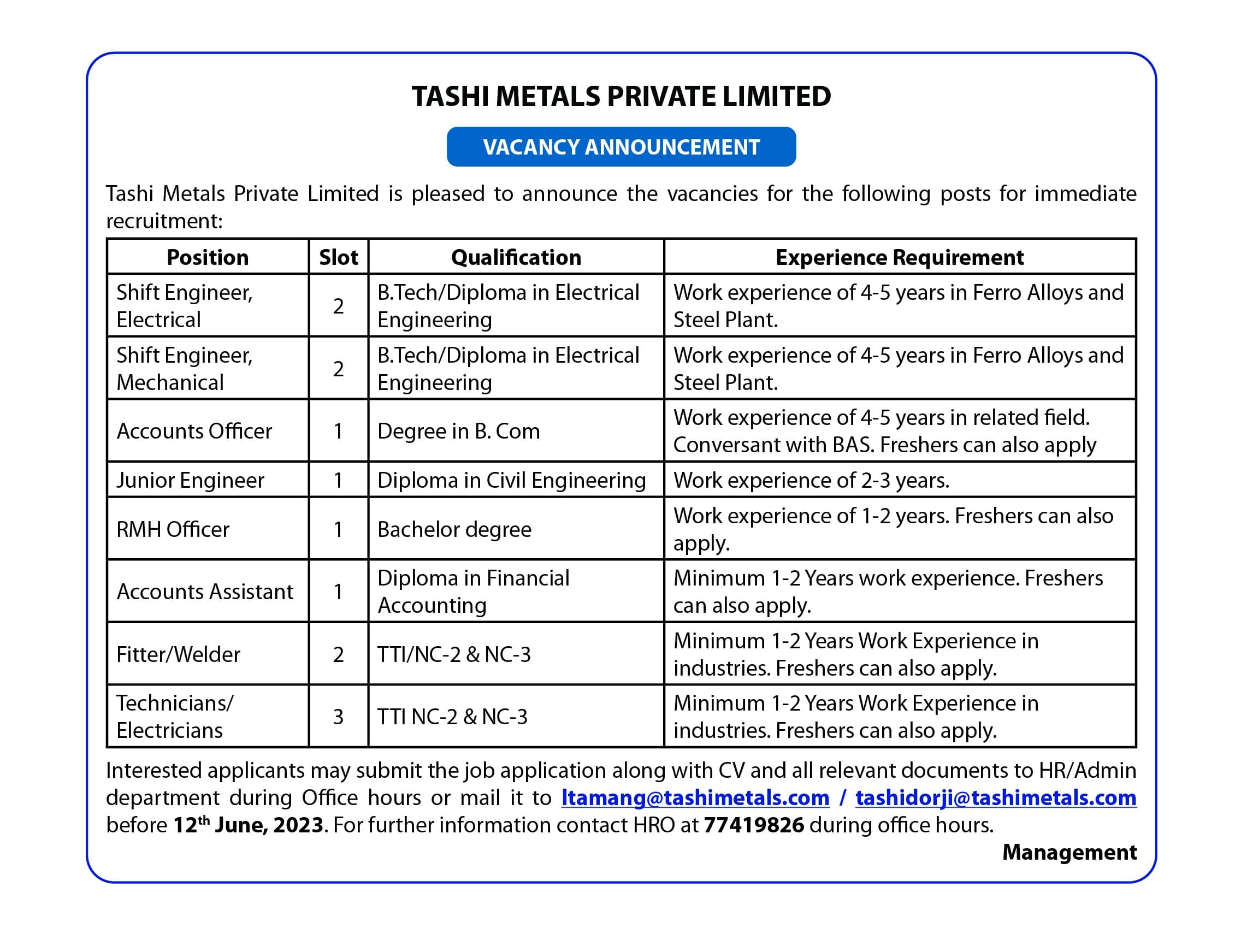
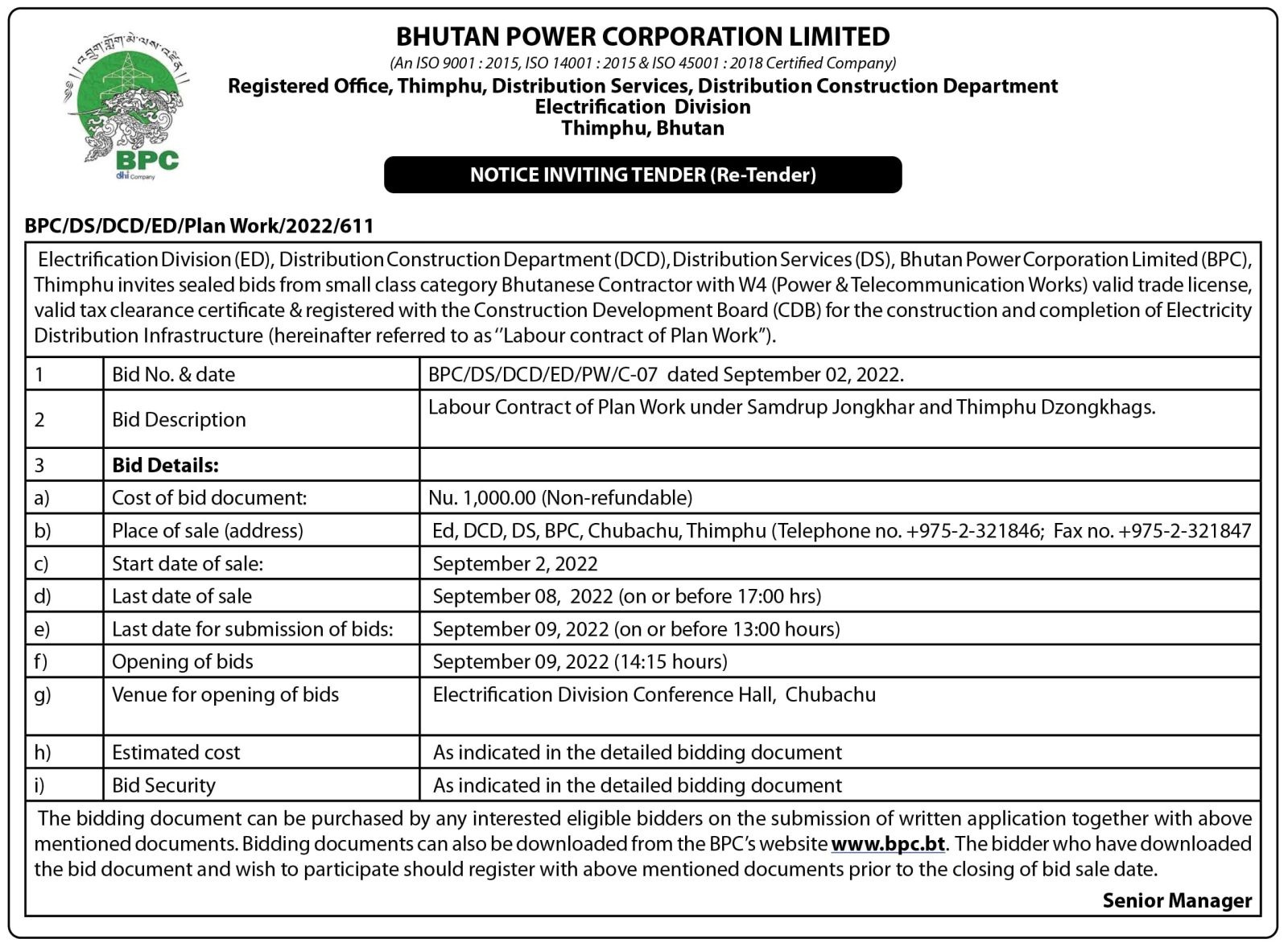
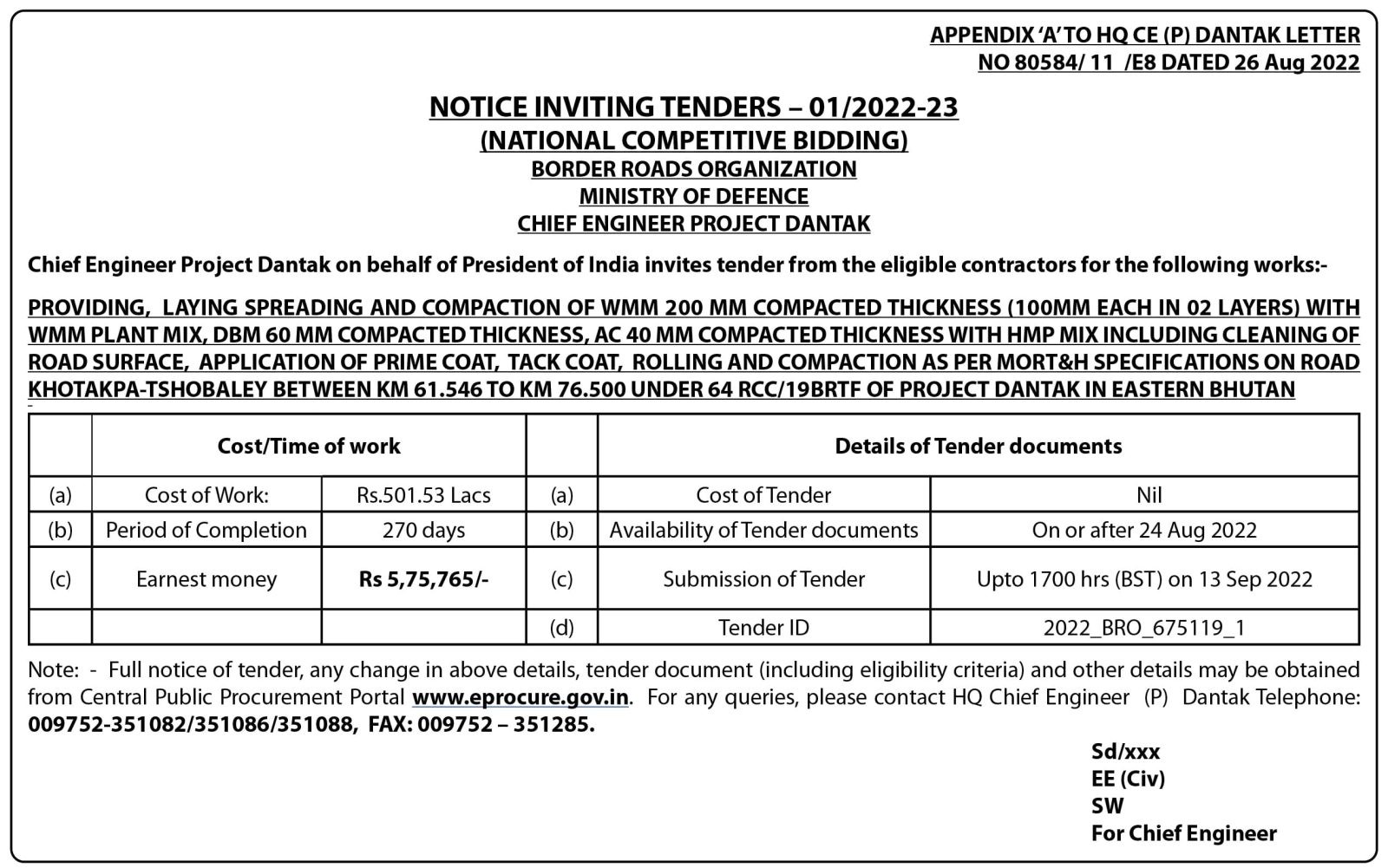
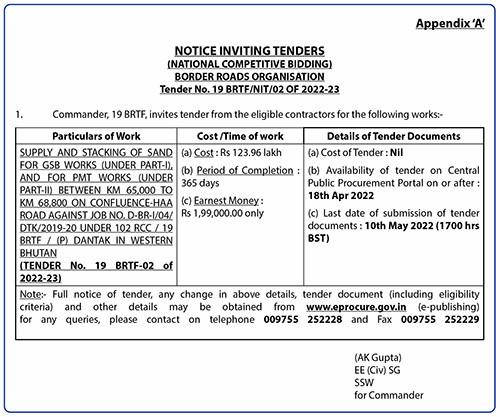
Around 5.6% of the country’s population encounter functioning difficulty with disabilities in seeing followed by mobility at 3.7% and hearing disability (3.5%), according to the Bhutan Living and Standards Survey (BLLS) 2017 released on Wednesday.
The prevalence of disability is defined as all the new and old cases of disability in a given population and time.
The report covers six functional domains or basic actions; seeing, hearing, mobility, cognition, self-care and communication with each domain having four responses from no difficulty, some difficulty, a lot of difficulty, and unable to do it at all which also corresponds to the degree of functioning ranging from mild to moderate to severe disability.
The report also reveals that disability among females is more prevalent than in males in almost all the domains and all forms of disability were slightly more prevalent in rural areas as compared to urban areas. However, the prevalence rate for persons with mild disability was almost equal for both male and female with 10.8% and 11% respectively. The prevalence of mild disability was high in rural areas with 12.4% than in urban areas (7.8%).
“People who experienced more severe functioning difficulties accounted for less than 1% in all the domains,” states the report.
The report also states that 2% of the people had moderate to severe disability, at least some difficulty in one domain, while 1% or 6,609 persons experienced severe disability.
Slightly more than 4% experienced some difficulties with multiple function or actions, which means that 29,760 people had some difficulties in at least two domains. The prevalence rate for persons with mild disability was estimated at about 11% or about 75,467 people in 2017.
On the other hand, in each degree of disability, prevalence was highest for persons aged 60 years and above ranging from about 1% in mild disability to 11% in moderate disability to about 4% in severe disability. There was slightly above 3% mild disability among younger persons aged 0-14 years.
The report also revealed that among the dzongkhags, the rate for mild disability was highest in Lhuntse (23.7%) and Bumthang with 19%. The lowest incidences of disability were lowest in Chhukha, Gasa and Pemagatshel with rates ranging from 5.4% to 6.2%.
The BLSS 2017, which was conducted in March and April this year, included 11,660 households with 48,639 persons. This sample represented a total of 164,011 households and 692,895 persons. Of the total number of estimated households in the country, that is 164,011, 3% reside in urban areas and 66% in rural areas.
The report states that the report provides important information pertaining to the social and economic conditions of the country, specifically demography, education, health, employment, housing, access to services, asset ownership, credit, self-perceived poverty and happiness.
Lucky Wangmo from Thimphu