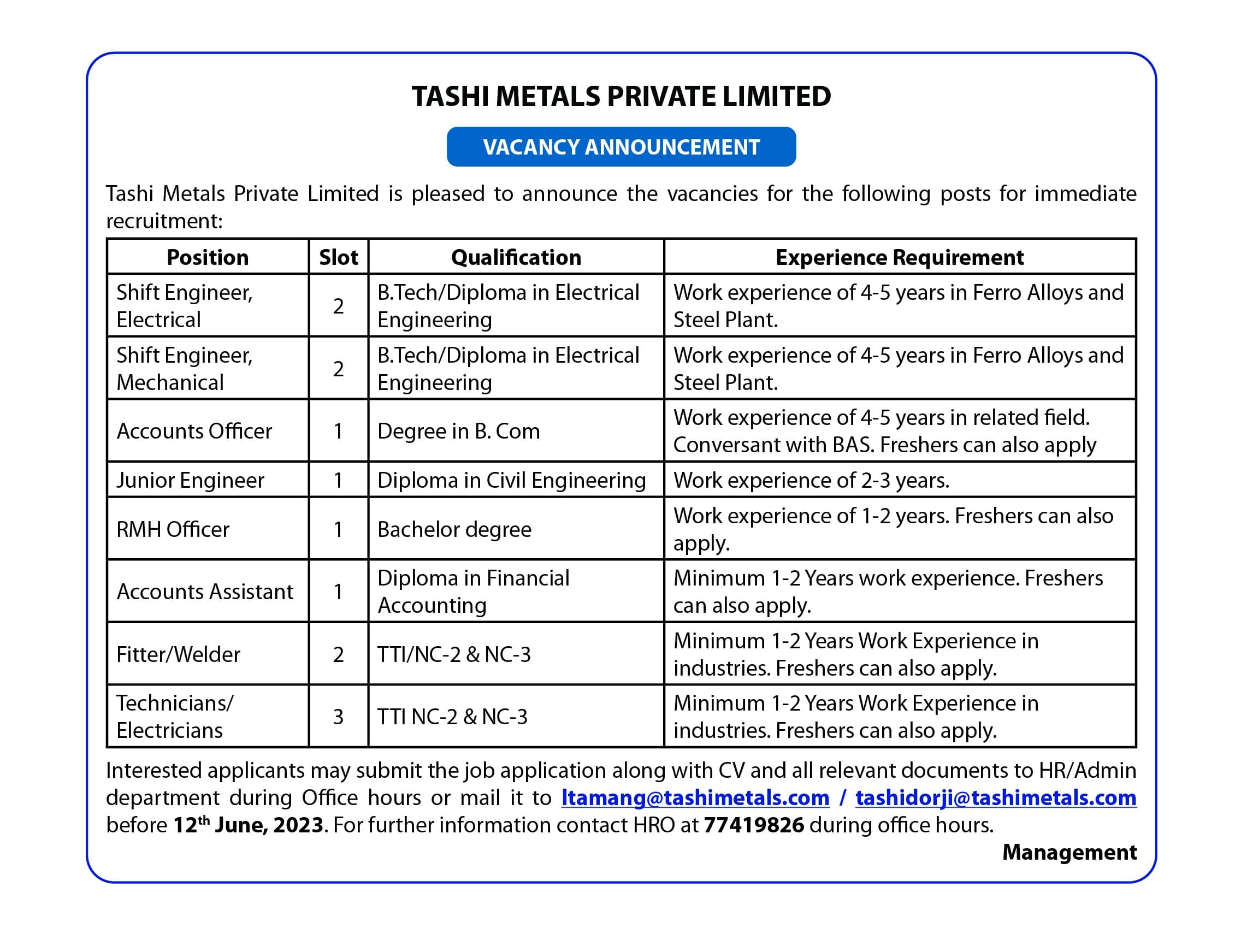
The debt in the hydropower sector constitutes the major portion of the total external debt with 73.5%, followed by Policy and Budget Support of 12.8% and Central Bank debt of 3.2%
The total public debt increased by Nu 2.49bn in the three months period from June to September end this year.
The total public debt stood at Nu 240.89bn as of September this year from the total public debt of Nu 238.39bn at June end this year.
According to the public debt situation quarter report as of September end, the total public debt accounted for 127.4% of the FY 2021-22 Gross Domestic Product estimate.
The report also states that the total public debt stock increased by Nu 2.49bn, which is 1% compared to the public debt stock on June 30, 2021. The increase was mainly attributed to the increase in T-Bills stocks by Nu 4,000mn. However, the rise in total public debt due to the increase in T-Bills stock was slightly offset by the drop in external debt stock.
However, the report states that the external debt decreased by Nu 1.5bn, which is around -0.7%, mainly on account of the MHPA repayment.
The second principal repayment of Nu 1.39bn was made in July 2021 based on the draft repayment protocol between the Government of Bhutan and the Government of India.
In addition, the depreciation of foreign currencies (USD, EUR, XDR, and JPY) in which CC debt is denominated also significantly reduced the Ngultrum value of CC debt stock, causing further decline in external debt stock.
It states that the domestic debt increased by Nu 4bn which is 23.4%, compared to the domestic debt stock on June 30, 2021. The increase was due to additional issuance of T-bills for the cash management during the quarter.
The total domestic debt stood on September 30th, 2021 at Nu 21.07bn, accounting for 11.1% of the GDP and 8.7% of total public debt stock.
The report states that hydropower debt stands at Nu 161.65bn which accounts for 73.5% of the external debt and accounted for 85.5% of the FY 2021-22 GDP estimate. The hydro debt stock comprises debt stock of six hydropower projects, namely the MHPA, Puna-I, Puna-II, Nikachu, Dagachu, and Basochu (upper and lower stage).
The non-hydro stood at Nu 58.17bn constituting 26.5% of the total external debt and 30.8% of the FY 2021-22 GDP estimate. The non-hydro debt to GDP of 30.8% is within the 35% threshold prescribed by the Public Debt Policy 2016.
The government debt accounted for 92.9% of the total external debt. The government debt includes debt on account of borrowings for budgetary activities, the development of hydropower projects, and project loans availed by the government and on-lent to public corporations.
The corporate debt of Nu 8.69bn accounted for 4% of the total external debt. The corporate debt pertains to debts directly contracted by the public corporations, such as a loan from the SDF availed by Drukair, and loans from ADB, EXIM Bank of India and State Bank of India contracted by Tangsibji Hydro Energy Limited.
The Central Bank debt, which is on account of Standby Credit Facility availed from the Government of India during the Rupee crunch in the year 2011-12, accounted for 3.2% of the total external debt. The RMA’s short-term swap arrangement of INR 14.541bn with the Reserve Bank of India has not been included.
As of September 30, 2021, the INR-denominated debt accounted for 70.2% of the total external debt, of which 95.5% was hydropower debt.
The INR-denominated debt decreased by Rs 621.052mn, compared to the INR debt stock on June 30, 2021. During the first quarter of the FY 2021-22(1 July 2021 to 30 Sept 2021), the GoI disbursed INR 369.3mn for Puna-I and INR 402.150mn for Puna-II.
After principal repayment of INR 1,392.502mn for the MHPA in July 2021, the INR-denominated value decreased by INR 621.052mn.
It states that the Convertible Currency (CC) debt stock stood at US $881.93mn, equivalent to Nu 65.43bn accounting for 29.8% of the total external debt.
The Ngultrum value of the CC debt stock decreased by Nu 880.032mn from the total CC debt stock of Nu 66.31bn (US$892.59million) on June 30 2021.
The Government of India remains the country’s largest creditor. As of September 30, 2021, 70% of Bhutan’s external debt was owed to GoI, followed by 14% to ADB and 12% to IDA. The rest, about 4%, were owed to the IFAD, JICA, GoA, and SDF combined.
The external debt servicing in the FY 2021-22 is expected to increase by more than 100% compared to the prior year external debt servicing, mainly because of full annual debt servicing for the MHPA and liquidation of Standby Credit Facility of INR 4bn.
As a result, despite the projected increase in exports during the FY 2021-22, the external debt service to exports ratio is expected to rise from 11.7% in the FY 2020-21 to 21.2% in the FY 2021-22.
Dechen Dolkar from Thimphu